Cuttlefish Malware : Steals Private Cloud Data
A Malware name , “Cuttlefish” is develop by Chinese hackers according to research of The Black Lotus Labs team. cuttlefish targeting networking equipment, particularly small office/home office (SOHO) routers. cuttlefish is developed to steal authentication material found in web requests (https) that transit the router from the adjacent local area network (LAN). it hijack DNS and HTTP both for connections to private IP space. more function like cuttlefish can interact with other devices on LAN and move material ore create a new agent. There’s code overlap with the HiatusRat malware, suggesting a connection to the People’s Republic of China’s interests. However, no shared victimology is observed, indicating concurrent activity clusters. Hackers using a malware to target routers and other networking equipment used by organizations in Turkey. Researchers from Lumen Technologies’ Black Lotus Labs said that the malware has been active since at least 27 July , 2023 and the latest campaign of infections ran from October 2023 to April 2024.Technical Details:
-
Malicious Files – Bash Script:
Network connections source : Black Lotus Labs The deployed bash script scans the device for information like directory listings, /etc contents, running processes, active connections, and mounts. It compresses this data into a file named “co.tmp.tar.gz” and uploads it to the domain hxxps://kkthreas[.]com/upload. It targets ARM-based devices primarily but has secondary paths for all major router architectures: i386, i386_i686, i386_x64, mips32, and mips64.
-
Malicious Files – Primary Payload, Cuttlefish:
-
Retrieval of RuleSets:
-
Credential Harvesting Functionality:
-
Logger and Data Transmission Function:
-
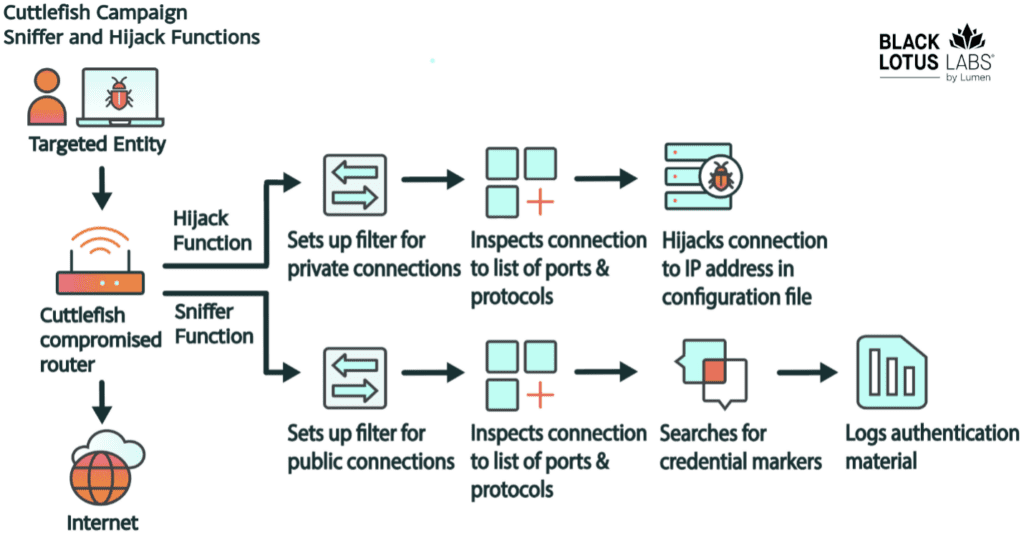
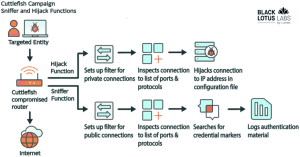
Hijack Functionality:
-
VPN Functionality:
-
Private Proxy Functionality:
Historical Context for the Campaigns:
Cuttlefish campaigns date back to August 2023, with extensive targeting observed in Turkey. Connections to C2 servers indicate compromises in various sectors, including telecommunications and data centers.Overlap with HiatusRat:
Cuttlefish shares code similarities with HiatusRat, suggesting a common developer or infrastructure. cuttlefish may modified version of hiatusRat.Black Lotus Labs Global Telemetry And Analysis:
Victimology predominantly involves Turkish-based IP addresses, with sporadic connections observed in other regions, including the US.Conclusion:
Cuttlefish represents a sophisticated evolution in malware targeting networking equipment, enabling passive eavesdropping and data theft. Recommendations include monitoring for IoCs and implementing security measures. This information is provided “as is” without any warranty or condition, and its use is at the end user’s risk. Full detailed article about cuttlefish malware by umen Technologies’ Black Lotus Labs Author : [ ultroidxTeam ] Thank you, remember me or bookmark this page for more cyber security related article… once again thank you ! feel free to leave your query in comment box.FAQs
Cuttlefish malware is a sophisticated threat designed to steal private cloud data by infiltrating cloud environments and exfiltrating sensitive information.
Cuttlefish malware operates stealthily, often evading detection until it has already compromised data. It can silently exfiltrate valuable information without leaving a trace.
The consequences of a Cuttlefish malware attack can include financial losses, reputational damage, legal liabilities, identity theft, and privacy violations.
Organizations can detect and prevent Cuttlefish malware by implementing robust security measures, including intrusion detection systems, endpoint protection solutions, security audits, employee training, encryption, access controls, and data loss prevention solutions.
Real-world incidents involving Cuttlefish malware highlight the importance of proactive cybersecurity measures, continuous monitoring, and threat intelligence to defend against evolving threats.